Rome Interesting Facts takes us on a captivating journey through the Eternal City’s rich history, architectural wonders, art, culture, and daily life, offering a glimpse into the grandeur that once was and the legacy that continues to inspire.
From the iconic Colosseum to the awe-inspiring Pantheon, Rome’s architectural marvels stand as testaments to the ingenuity and engineering prowess of ancient Romans. Their art and literature have left an indelible mark on Western civilization, while their religious beliefs and mythology have shaped countless works of art and literature.
Rome’s Historical Legacy
Rome’s history is a rich tapestry of civilization, conquest, and cultural achievement that has left an indelible mark on the world. From its humble beginnings as a small village on the banks of the Tiber River, Rome grew into a mighty empire that spanned three continents and ruled for over 500 years.
The history of Rome can be divided into several distinct eras, each with its own unique characteristics and contributions to the overall narrative. These eras include:
The Regal Period
- 753-509 BCE: The traditional founding of Rome by Romulus and Remus.
- Ruled by a series of seven kings, including Numa Pompilius, who established many of Rome’s religious and political institutions.
- The period ended with the overthrow of the last king, Tarquin the Proud, and the establishment of the Roman Republic.
The Roman Republic
- 509-27 BCE: A period of great expansion and consolidation for Rome.
- The Republic was characterized by a complex system of government that included a Senate, assemblies, and elected officials.
- Rome conquered vast territories, including much of Italy, Greece, and North Africa.
- The Republic ended with the rise of Julius Caesar and the establishment of the Roman Empire.
The Roman Empire
- 27 BCE-476 CE: The Roman Empire was one of the largest and most powerful empires in history.
- Ruled by a series of emperors, including Augustus, Nero, and Constantine.
- The Empire reached its greatest extent under Trajan in the 2nd century CE.
- The Empire began to decline in the 3rd century CE and eventually fell in 476 CE.
The Legacy of Rome
The legacy of Rome is vast and far-reaching. Roman law, architecture, engineering, and literature have all had a profound impact on Western civilization.
Rome’s history is a story of triumph and tragedy, of greatness and decline. It is a story that continues to fascinate and inspire people today.
Architectural Marvels
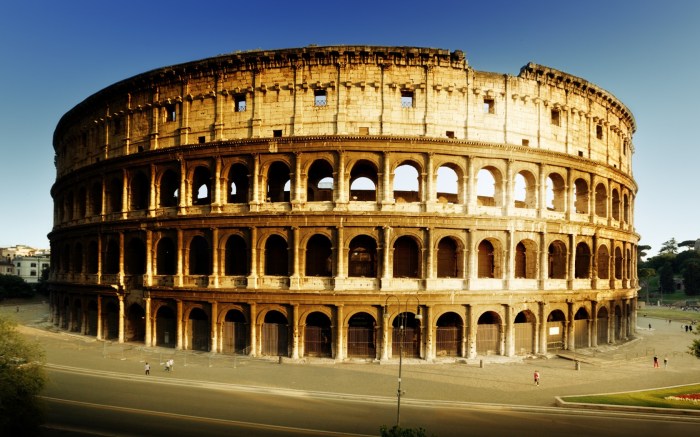

Rome is renowned for its architectural masterpieces that have stood the test of time and continue to inspire awe and wonder. These iconic structures showcase the engineering prowess and architectural brilliance of the ancient Romans.
From the colossal amphitheater of the Colosseum to the majestic dome of the Pantheon and the sprawling ruins of the Roman Forum, each landmark offers unique insights into the architectural ingenuity of its era.
The Colosseum
The Colosseum, an elliptical amphitheater completed in 80 AD, is the largest ancient amphitheater ever built. Its massive structure, capable of accommodating over 50,000 spectators, was designed to host gladiatorial contests and public spectacles. The Colosseum’s innovative use of arches and vaults, along with its intricate system of underground passages and elevators, reflects the advanced engineering techniques of the time.
The Pantheon
The Pantheon, constructed in 126 AD, is an architectural marvel renowned for its massive concrete dome. With a diameter of 43 meters, the dome is the largest unreinforced concrete dome in the world. The Pantheon’s interior is adorned with intricate coffered ceilings and a central oculus, which provides natural light to the vast space below.
Its architectural design has influenced numerous structures throughout history, including St. Peter’s Basilica in Rome.
The Roman Forum
The Roman Forum, located at the heart of ancient Rome, was the center of political, religious, and commercial life. Today, it is a sprawling archaeological site that offers a glimpse into the grandeur of the Roman Empire. The ruins of temples, basilicas, and government buildings, such as the Senate House and the Rostra, provide insights into the architectural styles and urban planning of the ancient city.
Rome’s storied past and enduring cultural legacy make it a treasure trove of fascinating trivia. From its iconic Colosseum to the bustling Trevi Fountain, the city is a living testament to its rich history. To fully immerse yourself in Rome’s captivating allure, consider a well-crafted itinerary like the rome itinerary 5 days . This comprehensive guide will lead you through the city’s most iconic landmarks, hidden gems, and culinary delights, ensuring an unforgettable Roman escapade.
| Feature | Colosseum | Pantheon | Roman Forum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural System | Arches and vaults | Concrete dome | Various, including arches, columns, and travertine blocks |
| Capacity | Over 50,000 spectators | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| Purpose | Gladiatorial contests and public spectacles | Temple | Political, religious, and commercial center |
| Iconic Feature | Elliptical shape and underground passages | Massive concrete dome and oculus | Ruins of temples, basilicas, and government buildings |
Art and Culture

Rome’s influence on art, literature, and philosophy has left an indelible mark on Western civilization. Roman artists and writers created masterpieces that continue to inspire and captivate audiences to this day.
In literature, Roman authors such as Virgil, Ovid, and Cicero produced works that are still widely read and studied today. Virgil’s epic poem “The Aeneid” is considered one of the greatest works of Latin literature, while Ovid’s “Metamorphoses” is a collection of myths that has influenced countless artists and writers throughout history.
In art, Roman sculptors created realistic and lifelike statues, often depicting gods, emperors, and other important figures. Roman architects designed and built some of the most iconic structures in the world, including the Colosseum, the Pantheon, and the Roman Forum.
Key Figures and Works of Roman Art and Literature
- Literature:
- Virgil: “The Aeneid”
- Ovid: “Metamorphoses”
- Cicero: “On the Nature of the Gods”
- Art:
- Sculptor: Michelangelo, “Pietà”
- Architect: Marcus Vitruvius Pollio, “De Architectura”
Religion and Mythology: Rome Interesting Facts
Ancient Rome had a complex and diverse religious system that evolved over time. It was a blend of traditional Roman beliefs, Greek mythology, and Eastern influences.
The Romans believed in a pantheon of gods and goddesses who controlled various aspects of life. They practiced a form of polytheism, worshipping multiple deities with different attributes and powers.
Major Roman Gods and Goddesses
- Jupiter: King of the gods, god of the sky and thunder
- Juno: Queen of the gods, goddess of marriage and childbirth
- Mars: God of war and agriculture
- Venus: Goddess of love and beauty
- Minerva: Goddess of wisdom and war
- Apollo: God of music, poetry, and prophecy
- Diana: Goddess of the hunt and wilderness
- Neptune: God of the sea
- Pluto: God of the underworld
- Proserpina: Goddess of the underworld and wife of Pluto
Roman mythology played a significant role in their society. It provided a framework for understanding the world and their place in it. Myths were used to explain natural phenomena, historical events, and human behavior.
Roman mythology also influenced their art and literature. Many works of Roman art depict scenes from mythology, and Roman literature is filled with references to mythical characters and stories.
Daily Life in Rome
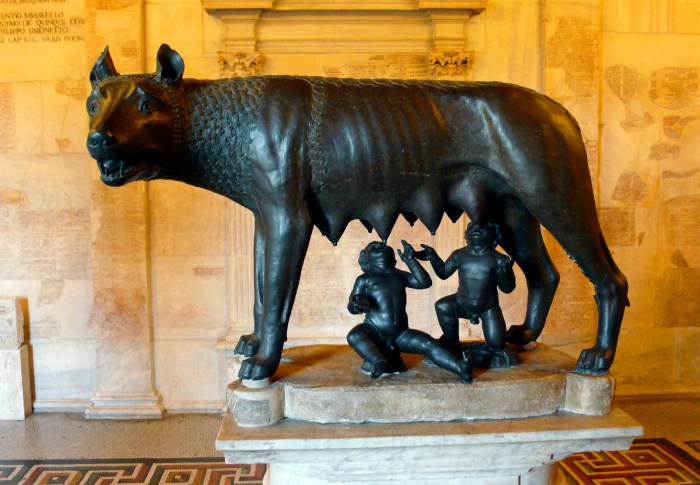

The daily life of ancient Romans was a complex and multifaceted affair, influenced by their social structure, cultural customs, and the rhythms of the city. From the bustling streets to the private homes, Romans navigated a world shaped by tradition, hierarchy, and the pursuit of pleasure.
The social structure of Rome was divided into three main classes: patricians, plebeians, and slaves. Patricians were the wealthy and aristocratic elite, who held most of the political power. Plebeians were the common people, who made up the majority of the population and worked in various trades and professions.
Slaves were the lowest class, with no rights or freedoms, and were often used as labor for both public and private purposes.
The daily routines of Romans varied depending on their social status. Patricians often began their day with a leisurely breakfast, followed by a visit to the baths or a morning stroll in the Forum. They might spend the afternoon attending to business or political matters, and the evening socializing at banquets or attending cultural events.
Plebeians, on the other hand, had to work for a living. Many worked as artisans, merchants, or laborers, while others were employed in the service of wealthy patrons. Women in Roman society were generally confined to the domestic sphere, responsible for raising children and managing the household.
However, some women did play a role in public life, such as attending religious festivals or participating in political demonstrations.
The following table provides a summary of the key aspects of daily life in Rome:
| Social Class | Daily Routine | Roles and Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Patricians | Leisurely breakfast, visit to the baths, business or political matters, socializing | Held political power, wealthy and aristocratic |
| Plebeians | Work in various trades and professions, service to wealthy patrons | Common people, majority of the population |
| Slaves | Used as labor for public and private purposes | Lowest class, no rights or freedoms |
The Roman Empire
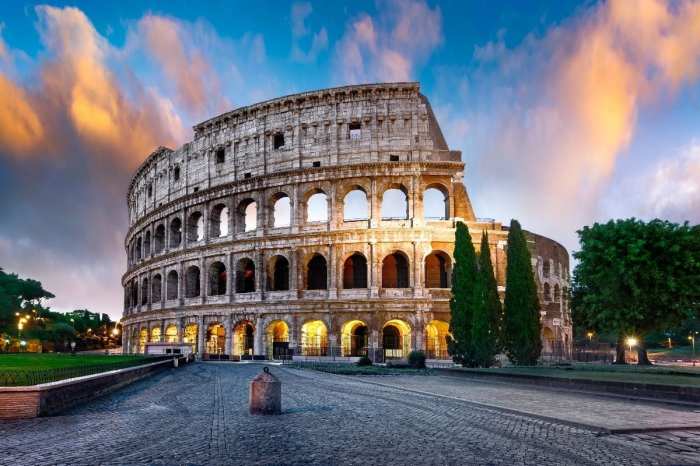

The Roman Empire, one of the most influential and enduring civilizations in human history, emerged from the city of Rome on the Italian Peninsula and grew to encompass vast territories across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East.
The empire’s expansion began in the 3rd century BCE with the Roman Republic’s conquest of neighboring Italian territories. Over the following centuries, Rome continued to expand through military campaigns, incorporating diverse regions such as Gaul (present-day France), Hispania (present-day Spain and Portugal), and Britannia (present-day United Kingdom).
The empire reached its greatest extent during the reign of Emperor Trajan in the early 2nd century CE, stretching from Britain in the north to Egypt in the south, and from Spain in the west to Mesopotamia in the east.
Rome’s rise to power was driven by a combination of factors, including its strong military, effective political system, and advanced infrastructure. The Roman army, renowned for its discipline and organization, played a crucial role in conquering and maintaining the empire’s vast territories.
The Roman Republic’s political system, which evolved over time from a monarchy to a republic and eventually to an empire, provided a framework for governance and stability.
The empire’s decline began in the 3rd century CE, marked by a combination of political instability, economic crises, and military pressures. The vastness of the empire made it difficult to govern effectively, and the empire faced increasing threats from external enemies such as the Germanic tribes and the Persians.
Internal divisions, including civil wars and the rise of powerful generals, further weakened the empire.
The Western Roman Empire collapsed in the 5th century CE, while the Eastern Roman Empire, known as the Byzantine Empire, continued to exist for another millennium.
Key Provinces and Territories, Rome interesting facts
The Roman Empire encompassed a vast array of provinces and territories, each with its own unique characteristics and contributions to the empire’s prosperity and culture.
Rome’s rich history and iconic landmarks never fail to captivate. For a change of pace, consider exploring kauai south shore rentals for a tranquil escape amidst stunning natural beauty. Afterward, delve back into Rome’s fascinating world, uncovering hidden gems and unraveling the secrets of its storied past.
- Italy:The heartland of the Roman Empire, Italy was home to the city of Rome and served as the administrative and political center of the empire.
- Gaul (France):A wealthy and prosperous province, Gaul was known for its agriculture, trade, and urban centers.
- Hispania (Spain and Portugal):A major source of minerals, Hispania was also home to thriving cities and a diverse population.
- Britannia (United Kingdom):The northernmost province of the empire, Britannia was known for its mineral resources and strategic location.
- Germania (Germany):A frontier province, Germania was the site of numerous military campaigns and was home to a variety of Germanic tribes.
- Aegyptus (Egypt):A vital province for its grain production, Aegyptus was also home to the ancient civilization of Egypt and its rich cultural heritage.
- Syria (Middle East):A crossroads of trade and culture, Syria was home to major cities such as Antioch and Damascus.
- Mesopotamia (Iraq):A fertile region, Mesopotamia was the site of ancient civilizations such as Sumer and Babylon.
Rome Today
The Eternal City continues to enchant visitors with its captivating blend of ancient ruins, vibrant culture, and modern urban life. As a renowned cultural and historical center, Rome attracts millions of tourists each year, drawn by its iconic landmarks, world-class museums, and vibrant art scene.
The preservation of Rome’s ancient heritage is a delicate balance between safeguarding its historical treasures and accommodating the needs of a modern metropolis. The city’s authorities work tirelessly to protect its archaeological sites, restore historical buildings, and manage the impact of tourism.
Top Attractions and Landmarks
Rome boasts an array of captivating attractions that reflect its rich history and cultural heritage:
| Landmark | Description |
|---|---|
| Colosseum | An iconic amphitheater that once hosted gladiatorial contests and public spectacles. |
| Roman Forum | The ruins of the ancient Roman city center, featuring temples, markets, and government buildings. |
| Vatican City | The smallest country in the world, home to St. Peter’s Basilica, the Vatican Museums, and the Sistine Chapel. |
| Trevi Fountain | A magnificent Baroque fountain where visitors toss coins to ensure their return to Rome. |
| Pantheon | An ancient temple with a remarkable dome, renowned for its architectural prowess. |
Last Word
Today, Rome remains a vibrant cultural and historical center, where ancient ruins coexist with modern life, and the echoes of the past resonate in every corner. Whether exploring the ruins of the Roman Forum or marveling at the grandeur of St.
Peter’s Basilica, Rome continues to captivate and inspire visitors from around the world.