Ancient rome background – Ancient Rome, a civilization that shaped the course of Western civilization, stands as a testament to human ingenuity, ambition, and cultural achievement. From its humble beginnings as a small settlement on the banks of the Tiber River to its rise as a vast empire spanning Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East, Rome’s story is one of conquest, innovation, and enduring influence.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of Ancient Rome, exploring its historical timeline, geographical setting, social structure, political system, economic activities, military prowess, architectural marvels, and artistic legacy. Prepare to be captivated as we uncover the secrets of this ancient civilization that continues to inspire and intrigue to this day.
Historical Timeline of Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome, a civilization renowned for its enduring legacy and profound impact on Western culture, spanned over a period of centuries, undergoing various transformative eras and significant events. Let’s delve into the historical timeline of Ancient Rome, exploring its major periods and pivotal moments.
Ancient Rome, a civilization that shaped the course of history, invites you to explore its ruins and monuments. From the iconic Colosseum to the opulent Roman Forum, every corner whispers tales of a glorious past. When planning your pilgrimage to this historical wonderland, the question of where to stay in Rome arises.
For an immersive experience, consider the charming neighborhoods of Trastevere or Monti. Explore our guide for recommendations on cozy guesthouses and luxurious hotels that will complement your journey through the annals of Ancient Rome.
Monarchy (753-509 BCE)
- 753 BCE: Traditional founding of Rome by Romulus and Remus.
- 6th century BCE: Etruscan influence and rule over Rome.
- 509 BCE: Overthrow of the Etruscan monarchy and establishment of the Roman Republic.
Roman Republic (509-27 BCE), Ancient rome background
The Roman Republic witnessed a period of significant territorial expansion, political reforms, and military conquests.
- 5th century BCE: Establishment of the Senate and the Comitia, laying the foundation for a representative government.
- 3rd century BCE: Punic Wars against Carthage, leading to Roman dominance in the Mediterranean.
- 2nd century BCE: Roman expansion into Greece and Asia Minor.
- 1st century BCE: Rise of Julius Caesar and the end of the Republic, paving the way for the Roman Empire.
Roman Empire (27 BCE-476 CE)
The Roman Empire, characterized by autocratic rule, vast territorial control, and cultural achievements, marked a new chapter in Roman history.
- 27 BCE: Augustus Caesar becomes the first Roman Emperor, ushering in the Pax Romana (Roman Peace).
- 1st century CE: Expansion of the Empire to its greatest extent, reaching from Britain to Egypt.
- 2nd century CE: Construction of iconic landmarks such as the Colosseum and the Pantheon.
- 3rd century CE: Crisis of the Third Century, a period of political instability and economic turmoil.
- 4th century CE: Constantine I legalizes Christianity, paving the way for its widespread adoption in the Empire.
- 395 CE: Division of the Roman Empire into the Western and Eastern Roman Empires.
- 476 CE: Fall of the Western Roman Empire, marking the end of Ancient Rome.
Geographical Setting of Ancient Rome
The Italian Peninsula, where Ancient Rome flourished, is a long, narrow stretch of land located in the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by the Alps to the north and the Apennines running down its center. The peninsula is surrounded by water on three sides, with the Tyrrhenian Sea to the west, the Adriatic Sea to the east, and the Ionian Sea to the south.
Impact of Geography
The geography of the Italian Peninsula had a profound impact on the development of Ancient Rome. The mountainous terrain provided natural barriers against invasion, while the coastline offered access to trade and commerce. The peninsula’s central location in the Mediterranean Sea made it a crossroads of trade routes, connecting Europe, Africa, and Asia.
The Tiber River, which flows through the center of the peninsula, provided a vital source of water and transportation. The river’s mouth at Ostia served as a major port, facilitating trade and communication with other regions.
Ancient Rome, a civilization that has left an enduring legacy, had a profound impact on the world. Its empire spanned vast territories, and many of its iconic sites still stand today. From the grandeur of the Colosseum to the intricate mosaics of Pompeii, ancient Roman sites offer a glimpse into the architectural marvels and societal complexities of this ancient civilization.
They provide valuable insights into the lives, beliefs, and artistic achievements of the Romans, allowing us to appreciate the enduring influence of their empire.
The fertile plains of Latium, where Rome was located, provided ample agricultural land for the growing population. The surrounding hills offered strategic defensive positions, making Rome less vulnerable to attack.
Roman Society and Culture
Roman society was highly structured and hierarchical, with a complex system of social classes and family relationships. Religion played a central role in Roman life, with a pantheon of gods and goddesses who were believed to control all aspects of human existence.
Social Structure
Roman society was divided into three main classes: patricians, plebians, and slaves.
- Patricianswere the wealthy, landowning elite who held most of the power and prestige in Roman society.
- Plebianswere the common people who made up the majority of the population. They were farmers, artisans, merchants, and soldiers.
- Slaveswere the lowest class in Roman society. They were owned by patricians and plebians and had no rights.
Family Life
The Roman family was the basic unit of society. It was headed by the father, who had absolute authority over his wife, children, and slaves. The family was responsible for providing for its members and for passing on Roman traditions and values.
Religious Beliefs
The Romans were a polytheistic people who believed in a pantheon of gods and goddesses. The most important gods were Jupiter, the king of the gods; Juno, his wife; and Minerva, the goddess of wisdom. The Romans believed that the gods controlled all aspects of human life, from birth to death.
Roman Government and Politics: Ancient Rome Background

The Roman government was a complex and evolving system that underwent significant changes over time. Initially, Rome was ruled by kings, but after the overthrow of the monarchy in 509 BC, the government transitioned to a republic, characterized by a balance of power between various institutions and offices.
The Senate
The Senate was the most important political body in the Roman Republic. It consisted of elder statesmen who had previously held high office and served as advisors to the government. The Senate had the power to make laws, declare war, and approve treaties.
It also played a crucial role in the election of magistrates and the administration of the provinces.
Consuls
The consuls were the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic. They were elected annually and held supreme executive and military authority. The consuls commanded the army, presided over the Senate, and proposed laws to the people’s assembly for approval.
Emperors
In the late Republic, the rise of powerful generals led to the gradual erosion of republican institutions. By the 1st century BC, Julius Caesar had emerged as the dominant figure in Roman politics and established himself as dictator. After Caesar’s assassination, his adopted son, Augustus, became the first Roman emperor.
The emperors gradually concentrated more and more power in their hands, eventually transforming the Roman Republic into an empire.
Roman Economy and Trade

The Roman economy was one of the most advanced and sophisticated in the ancient world. It was based on a complex system of trade and commerce that stretched from the shores of the Mediterranean Sea to the borders of the Roman Empire.The
Romans were skilled merchants and traders, and they developed a vast network of trade routes that connected them with all parts of the known world. They traded a wide variety of goods, including food, wine, olive oil, textiles, and slaves.
Roman coins were widely accepted as currency throughout the empire, and they were used to facilitate trade and commerce.
Roman Coins
The Romans minted a variety of coins, each with its own value. The most common coins were the denarius, the sestertius, and the as. The denarius was the most valuable coin, and it was used for large transactions. The sestertius was worth four asses, and it was used for smaller transactions.
The as was the smallest coin, and it was used for everyday purchases.The value of Roman coins varied over time, but the following table provides a general overview of their worth:| Coin | Value ||—|—|| Denarius | 10 asses || Sestertius | 4 asses || As | 1 ass |
Roman Military and Warfare

The Roman army was a highly organized and disciplined force that played a crucial role in the expansion of the Roman Empire. The army was divided into legions, each consisting of approximately 5,000 soldiers. Legions were further subdivided into cohorts and centuries, with each century commanded by a centurion.The
Roman army’s tactics were based on the principle of the manipular formation. In this formation, the army was divided into three lines. The first line consisted of young and inexperienced soldiers, the second line of more experienced soldiers, and the third line of veterans.
The first line would engage the enemy in close combat, while the second and third lines would provide support and reinforcement.
Roman Military Victories
The Roman army’s superior organization and tactics led to a series of military victories that expanded the Roman Empire. Some of the most notable Roman military victories include:
- The Punic Wars (264-146 BC): The Punic Wars were a series of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage. The Romans emerged victorious from these wars, gaining control of North Africa and the western Mediterranean.
- The Gallic Wars (58-50 BC): The Gallic Wars were a series of campaigns fought by Julius Caesar against the Gallic tribes. Caesar’s victories in these wars brought Gaul (present-day France) under Roman control.
- The Battle of Actium (31 BC): The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between Octavian and Mark Antony. Octavian’s victory in this battle led to the establishment of the Roman Empire.
Roman Architecture and Engineering
Roman architecture and engineering showcased the empire’s exceptional ingenuity and creativity. From towering aqueducts to opulent palaces, Roman structures were renowned for their grandeur, functionality, and enduring legacy.
Architectural Styles and Techniques
Roman architecture drew inspiration from Greek and Etruscan traditions, evolving into a distinctive style characterized by:
- Arches and Vaults:Romans mastered the use of arches and vaults, allowing them to construct vast and stable structures with minimal materials.
- Concrete:Roman concrete, a mixture of volcanic ash, lime, and water, provided strength and durability to their structures, enabling the construction of monumental buildings.
- Domes:The Pantheon, with its iconic hemispherical dome, is a testament to Roman prowess in dome construction.
Famous Roman Structures
Ancient Rome left behind a treasure trove of architectural wonders that continue to inspire awe and admiration:
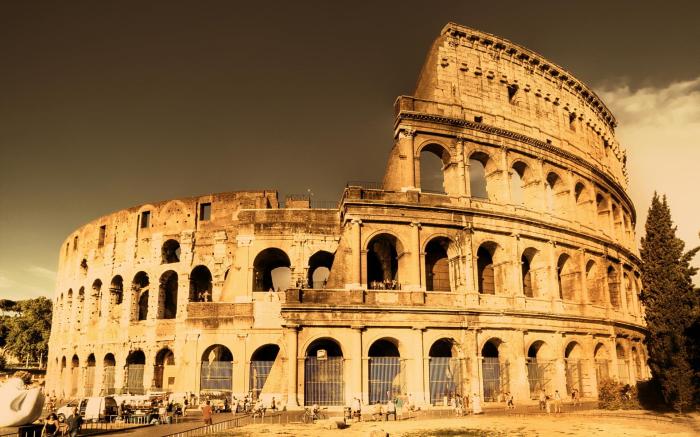
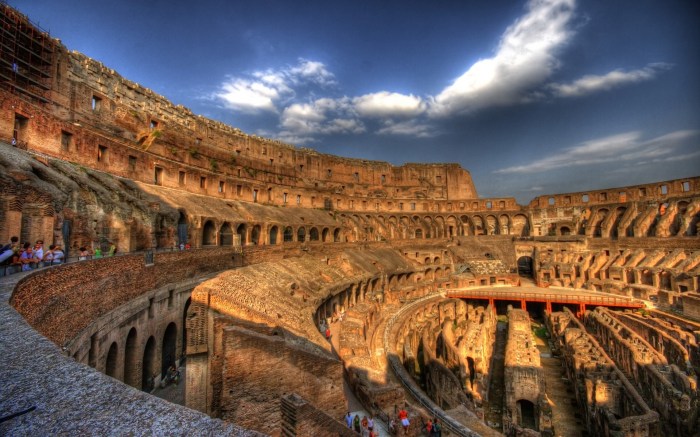
- Colosseum:The largest amphitheater ever built, hosting gladiatorial contests and public spectacles.
- Pantheon:A temple dedicated to all Roman gods, renowned for its massive concrete dome and oculus (circular opening).
- Roman Forum:The political and social heart of ancient Rome, featuring temples, basilicas, and public buildings.
Roman Art and Literature
Roman art and literature flourished during the Roman Empire, showcasing the creativity and cultural achievements of this ancient civilization.
Roman Art
Roman art was influenced by both Greek and Etruscan traditions, resulting in a unique blend of styles. Roman sculptors excelled in creating realistic and expressive statues, often depicting emperors, gods, and other important figures. Roman paintings, preserved in the ruins of Pompeii and Herculaneum, display a variety of styles, from realistic portraits to intricate mythological scenes.
Roman mosaics, made from small pieces of colored stone or glass, were used to decorate floors and walls, creating stunning and colorful designs.
Roman Literature
Roman literature emerged in the 3rd century BCE, heavily influenced by Greek literature. Roman authors produced a wide range of works, including epic poems, historical accounts, comedies, and tragedies. One of the most famous Roman literary works is the Aeneid by Virgil, an epic poem that tells the story of Aeneas, a Trojan hero who founded Rome.
Another notable work is the Metamorphoses by Ovid, a collection of mythological stories.
Conclusion

Our journey through Ancient Rome has shed light on the remarkable achievements and complexities of this influential civilization. From its humble origins to its imperial grandeur, Rome’s legacy continues to resonate in our world today. Its contributions to law, government, architecture, engineering, literature, and art have left an enduring mark on human history.
As we close this chapter, let us remember the lessons learned from Ancient Rome. Its triumphs and challenges offer valuable insights into the nature of human society, the importance of innovation, and the enduring power of human spirit. May the legacy of Rome continue to inspire us to strive for greatness and to build a better future for generations to come.