Family in Ancient Rome unveils the intricate tapestry of Roman society, where patriarchal values shaped family structures and religious beliefs influenced everyday life. Embark on a journey through time as we explore the roles, responsibilities, and challenges faced by Roman families.
From the legal authority of the paterfamilias to the sacred rituals honoring household gods, this narrative delves into the diverse aspects of family life in ancient Rome, shedding light on the foundation that supported the rise and fall of one of history’s most enduring civilizations.
Marriage and Family Formation

Marriage in ancient Rome was a complex institution with legal, social, and religious implications. The process of marriage involved several steps, including betrothal, the wedding ceremony, and the consummation of the marriage.
Legal Requirements
To be legally valid, a marriage in ancient Rome had to meet certain requirements. Both parties had to be Roman citizens, of marriageable age (14 for girls and 16 for boys), and not already married. Additionally, the marriage had to be approved by the paterfamilias (head of the household) of both parties.
Ceremonies and Customs
The wedding ceremony typically consisted of three parts: the betrothal, the wedding feast, and the consummation. The betrothal was a formal agreement between the two families, in which the groom gave the bride a ring and a dowry. The wedding feast was a large celebration attended by both families and friends.
The consummation of the marriage took place after the feast, when the bride and groom retired to their bedroom.
The family unit was the cornerstone of ancient Roman society, with strong bonds and traditions shaping their daily lives. Exploring life in ancient Rome provides a fascinating glimpse into the intricate roles and responsibilities of family members, from the paterfamilias to the youngest child.
The family’s influence extended beyond the household, playing a vital role in shaping the political and social landscape of ancient Rome.
Types of Marriage
There were two main types of marriage in ancient Rome: patrician and plebeian marriages. Patrician marriages were between members of the patrician class, the elite ruling class of Rome. Plebeian marriages were between members of the plebeian class, the common people of Rome.
Patrician marriages were considered more prestigious and carried more legal rights and obligations than plebeian marriages.
Role of Family
The family played a significant role in arranging marriages in ancient Rome. The paterfamilias of each family had the final say in whether or not a marriage would take place. Marriages were often arranged for political or financial reasons, rather than for love.
Importance of Dowry
The dowry was an important part of marriage in ancient Rome. It was a sum of money or property that the bride’s family gave to the groom’s family as a contribution to the marriage. The size of the dowry was often a reflection of the bride’s family’s wealth and status.
Childbirth and Childrearing
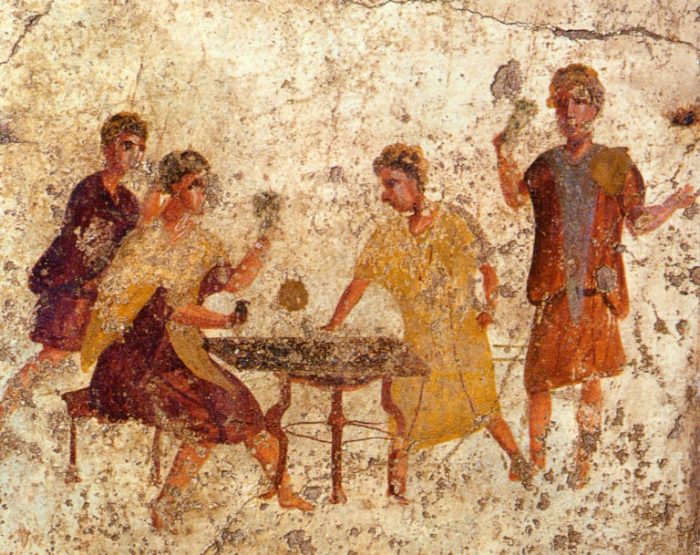

Childbirth in ancient Rome was a perilous event, with a high mortality rate for both mothers and infants. The Romans believed that childbirth was a sacred and dangerous process, and they surrounded it with a variety of rituals and practices.Midwives
played a central role in childbirth, assisting with the delivery and providing care for the mother and child. They used a variety of techniques to ease the pain of labor, including massage, warm baths, and herbal remedies. Midwives also used amulets and charms to protect the mother and child from evil spirits.
Childrearing, Family in ancient rome
Roman children were typically raised by their mothers and wet nurses. Wet nurses were often slaves or poor women who were hired to breastfeed and care for infants. The use of wet nurses was common among wealthy families, as it allowed mothers to continue their social and political activities.Education
was an important part of childrearing in ancient Rome. Boys were typically sent to school, where they learned reading, writing, and arithmetic. Girls were typically educated at home by their mothers or private tutors.The extended family played an important role in childrearing in ancient Rome.
Grandparents, aunts, and uncles often lived with or near the nuclear family, and they helped to care for and educate the children.
Infant Mortality
The infant mortality rate in ancient Rome was very high. As many as one in three infants died before their first birthday. The most common causes of infant death were malnutrition, disease, and exposure.Roman families coped with the loss of children in a variety of ways.
Some families buried their children in elaborate tombs, while others cremated them and kept their ashes in urns. Families also mourned the loss of their children through rituals and festivals.
Family Law and Inheritance: Family In Ancient Rome

Roman family law was a complex and evolving body of regulations that governed the legal relationships between family members. It covered a wide range of topics, including adoption, divorce, and inheritance. Roman law placed great emphasis on the importance of the family unit, and it sought to protect the rights and responsibilities of all family members.
In ancient Rome, the family was a central institution, providing social, economic, and political support. The pater familias, or head of the household, held absolute authority over his wife, children, and slaves. The extended family often lived together in a single household, and members were expected to support each other throughout their lives.
The concept of family was so important to the Romans that they even had a god, Janus, who was responsible for protecting families. If you’re planning a trip to Hawaii, consider booking a north shore kauai airbnb to experience the beauty of the island and learn more about its rich history.
The north shore of Kauai is home to some of the most beautiful beaches in the world, and there are plenty of activities to keep you busy, from swimming and sunbathing to hiking and biking. You’ll also find a variety of restaurants and shops in the area, so you can easily find something to suit your needs.
Whether you’re looking for a romantic getaway or a fun-filled family vacation, a north shore kauai airbnb is the perfect choice.
Adoption
Adoption was a common practice in ancient Rome. It allowed a couple who could not have children of their own to create a family. Adoption also provided a way for wealthy families to ensure that their property would be passed down to their descendants.
The legal process of adoption was relatively simple. The adoptive parents would make a formal request to the praetor, who would then issue a decree granting the adoption. The adopted child would then become a full member of the adoptive family, with all the rights and responsibilities of a natural child.
Divorce
Divorce was also relatively common in ancient Rome. It was available to both men and women, and it could be granted for a variety of reasons, including adultery, cruelty, and desertion. The legal process for divorce was similar to that for adoption.
The divorcing couple would make a formal request to the praetor, who would then issue a decree granting the divorce. The divorced couple would then be free to remarry.
Inheritance
Inheritance was a complex and important part of Roman law. It governed the distribution of property after a person’s death. The legal rules of inheritance were based on the principle of primogeniture, which meant that the eldest son inherited the majority of the property.
However, there were a number of exceptions to this rule. For example, a father could disinherit his eldest son if he had committed a serious crime. He could also leave his property to his wife or to his other children.
Family and Religion
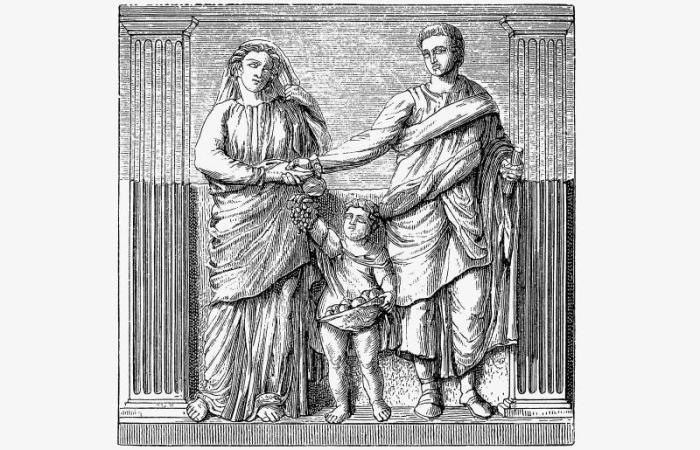

Religion played a pivotal role in ancient Roman family life, permeating every aspect from daily rituals to major life events. The family was considered a sacred unit, and its members shared a common religious bond.
The Romans believed in a pantheon of gods, including household gods called Lares and Penates, who were responsible for protecting the family and its well-being. Families had their own shrines where they performed daily rituals, such as offering prayers, sacrifices, and libations to their household gods.
Worship of Household Gods
The worship of household gods was an essential part of Roman family life. Each family had its own unique set of gods, which were passed down from generation to generation. The Lares were believed to be the spirits of deceased ancestors, while the Penates were the gods of the pantry and household supplies.
Families would make offerings to their household gods on a daily basis, and they would also hold special ceremonies on important occasions, such as births, marriages, and deaths. These rituals helped to strengthen the bond between the family and its gods and to ensure their protection.
Family Rituals
In addition to the worship of household gods, Roman families also observed a number of other religious rituals. These rituals marked important life events, such as births, marriages, and deaths, and they helped to reinforce the family’s social and religious identity.
For example, when a child was born, the father would hold the child up to the sky and pray to the gods for its health and well-being. When a couple got married, they would exchange vows in front of a priest or magistrate, and they would also make offerings to the gods to ensure a happy and prosperous marriage.
Influence of Religious Beliefs on Family Practices
Religious beliefs had a significant influence on Roman family practices. For example, the Romans believed that it was important to have children, as they were needed to carry on the family line and to worship the household gods. As a result, Roman families often had large numbers of children.
Religious beliefs also influenced the types of marriages that were allowed. For example, it was forbidden for Romans to marry their close relatives, as this was considered to be incest. Additionally, it was forbidden for Romans to marry foreigners, as this was considered to be a threat to the purity of the Roman race.
Role of the Vestal Virgins
The Vestal Virgins were a group of six young women who were chosen to serve as priestesses of the goddess Vesta. The Vestal Virgins were responsible for tending to the sacred fire of Vesta, which was believed to be the symbol of the Roman state.
They also performed other religious rituals and ceremonies.
The Vestal Virgins were highly respected in Roman society, and they enjoyed a number of privileges. They were exempt from the usual restrictions on women, such as the requirement to marry and have children. They also had the right to vote and to hold public office.
End of Discussion

In the twilight of ancient Rome, the family remained a steadfast pillar, adapting to changing social and political landscapes. The legacy of Roman family values continues to resonate today, shaping our understanding of kinship, marriage, and the enduring power of familial bonds.